✨ 新增内容 AI 共创
AI播客:函数调用:AI告别纸上谈兵,真正走向现实行动
💡 大白话解释 用最简单的话说清楚 ▶
什么是 Function Calling(函数调用) 实际例子:
例子 1:查天气
你:北京明天会下雨吗?
AI:[调用 get_weather(city="北京", date="明天")]
系统:{"condition": "晴", "rain_probability": 10%}
AI:明天北京是晴天,下雨概率只有 10%,不太会下雨。
例子 2:发邮件
你:给张三发封邮件,主题"会议通知",内容"明天下午 3 点开会"
AI:[调用 send_email(
to="zhangsan@example.com",
subject="会议通知",
body="明天下午 3 点开会"
)]
系统:邮件已发送
AI:已经给张三发送邮件了。
例子 3:写代码并运行
你:帮我计算 1 到 100 的和
AI:[调用 run_python_code(code="sum(range(1, 101))")]
系统:返回 5050
AI:1 到 100 的和是 5050。
例子 4:多步骤任务
你:帮我查一下特斯拉股价,如果涨了就买 10 股
AI:
1. [调用 get_stock_price(symbol="TSLA")]
系统:当前价格 $250,昨日收盘 $240
2. AI 判断:涨了 $10
3. [调用 buy_stock(symbol="TSLA", quantity=10)]
系统:已购买 10 股特斯拉,总价 $2500
AI:特斯拉今天涨到 $250(涨了 $10),已帮你买入 10 股,花费 $2500。
Function Calling vs 普通对话:
功能 普通对话 Function Calling 查实时数据 ❌ 瞎猜 ✅ 真实查询 执行操作 ❌ 只能说 ✅ 真的能干 联网搜索 ❌ 不行 ✅ 可以 调用 API ❌ 不行 ✅ 可以 操作数据库 ❌ 不行 ✅ 可以
技术流程(给开发者看的):
第 1 步:定义工具
tools = [
{
"name" : "get_weather" ,
"description" : "获取指定城市的天气" ,
"parameters" : {
"city" : "城市名(如:北京)" ,
"date" : "日期(可选,默认今天)"
}
}
] 第 2 步:调用 AI
response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [ { "role" : "user" , "content" : "北京明天天气" } ] ,
tools = tools # 告诉 AI 可用的工具
) 第 3 步:AI 返回调用请求
{
"tool_calls" : [ {
"function" : {
"name" : "get_weather" ,
"arguments" : "{\"city\": \"北京\", \"date\": \"明天\"}"
}
} ]
} 第 4 步:执行工具并返回结果
# 你的代码执行工具
result = get_weather ( city = "北京" , date = "明天" )
# 结果:{"temp": 20, "condition": "晴"}
# 把结果返回给 AI
final_response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [
{ "role" : "user" , "content" : "北京明天天气" } ,
{ "role" : "assistant" , "tool_calls" : [ . . . ] } ,
{ "role" : "tool" , "content" : str ( result ) } # 工具返回的结果
]
) 第 5 步:AI 生成最终回复
为什么这么重要?
没有 Function Calling:
AI 只能"纸上谈兵"
所有信息都是训练数据里的(可能过时、不准确)
无法操作系统、无法联网
有了 Function Calling:
AI 成为"真正的助手"
可以实时查询数据
可以自动化操作(发邮件、订票、写代码并运行)
可以连接任何 API 和系统
现实案例:
ChatGPT Plugins :通过 Function Calling 调用外部服务(订餐、订酒店、查航班)GitHub Copilot :调用代码分析工具客服机器人 :查订单、退款、转接人工智能家居 :控制灯光、空调、窗帘
常见误区:
误区 1:"Function Calling = 让 AI 写代码"
不对!Function Calling 是让 AI 调用你预定义的函数
AI 只负责决定"调用哪个函数、传什么参数"
具体执行还是你的代码
误区 2:"所有 AI 都能 Function Calling"
不对!只有支持的模型才行
支持:GPT-4、GPT-3.5-turbo、Claude 3+、Gemini 1.5+
不支持:老模型(GPT-3)
误区 3:"Function Calling 是自动的"
不对!你需要:
定义工具(告诉 AI 有哪些函数可用)
解析 AI 的调用请求
执行函数
把结果返回给 AI
说白了,Function Calling 就是让 AI 从"只会说"变成"能干活"——它能调用你提供的工具,真正完成任务,而不只是"嘴上说说"。
预计阅读时间: 8 分钟
Function Calling(函数调用),也称为 Tool Use(工具使用),是大型语言模型(LLM)的一项关键能力:让模型能够调用外部工具和 API ,从而突破"只能生成文本"的限制,实现真正的任务执行。
核心概念
为什么需要 Function Calling?
传统 LLM 的局限:
❌ 无法访问实时数据(如股票价格、天气)
❌ 无法执行操作(如发送邮件、订票)
❌ 无法联网搜索
❌ 知识截止日期后的信息一无所知
Function Calling 的能力:
✅ 调用 API 获取实时数据
✅ 执行系统操作
✅ 联网搜索
✅ 操作数据库
✅ 运行代码
定义
Function Calling 是 LLM 的一种特殊输出格式:
输入:用户请求 + 可用工具列表
输出:结构化的函数调用请求 (而非自然语言)
执行:开发者接收请求 → 执行函数 → 返回结果给 LLM
最终:LLM 根据结果生成用户友好的回复
工作流程
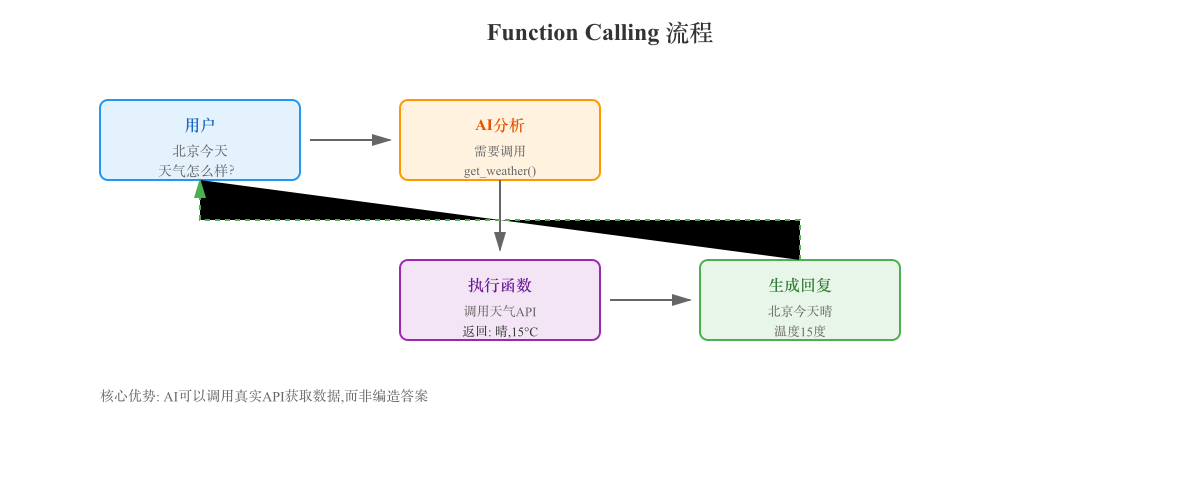
完整流程示意
用户:"北京今天天气怎么样?"
↓
开发者:定义可用工具
tools = [{
name: "get_weather",
description: "获取指定城市天气",
parameters: {city: string, date: string}
}]
↓
调用 LLM(传入工具列表)
↓
LLM 分析:需要调用 get_weather
↓
LLM 输出:
{
"function": "get_weather",
"arguments": {"city": "北京", "date": "today"}
}
↓
开发者代码:执行函数
result = get_weather("北京", "today")
# 返回 {"temp": 15, "condition": "多云"}
↓
将结果返回给 LLM
↓
LLM 生成最终回复:
"北京今天多云,温度 15 度。"
↓
返回给用户
关键步骤
步骤 1:定义工具(Tools Definition)
告诉 LLM 有哪些工具可用。
OpenAI 格式:
{
"tools" : [
{
"type" : "function" ,
"function" : {
"name" : "get_weather" ,
"description" : "获取指定城市的天气信息" ,
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"city" : {
"type" : "string" ,
"description" : "城市名称,如:北京、上海"
} ,
"date" : {
"type" : "string" ,
"description" : "日期,如:today, tomorrow, 2025-01-15" ,
"enum" : [ "today" , "tomorrow" ]
}
} ,
"required" : [ "city" ]
}
}
}
]
} 关键字段:
name:函数名称description:函数功能描述(非常重要 ,LLM 靠这个理解工具用途)parameters:参数定义(JSON Schema 格式)required:必需参数
步骤 2:调用 LLM
import openai
response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [
{ "role" : "user" , "content" : "北京明天天气怎么样?" }
] ,
tools = tools , # 传入工具定义
tool_choice = "auto" # auto | none | {"type": "function", "function": {"name": "..."}}
) tool_choice 参数:
auto:让 LLM 自动判断是否需要调用工具(默认)none:强制 LLM 不调用工具{"type": "function", "function": {"name": "get_weather"}}:强制调用特定工具
步骤 3:解析 LLM 响应
message = response . choices [ 0 ] . message
# 检查是否有工具调用
if message . tool_calls :
tool_call = message . tool_calls [ 0 ]
function_name = tool_call . function . name # "get_weather"
function_args = json . loads ( tool_call . function . arguments )
# {"city": "北京", "date": "tomorrow"} 步骤 4:执行函数
# 你的实际函数实现
def get_weather ( city , date = "today" ) :
# 调用天气 API
api_response = requests . get ( f"https://api.weather.com/..." ,
params = { "city" : city , "date" : date } )
return api_response . json ( )
# 执行函数
if function_name == "get_weather" :
result = get_weather ( ** function_args )
# 结果:{"temp": 20, "condition": "晴"} 步骤 5:将结果返回给 LLM
# 构建新的消息历史
messages = [
{ "role" : "user" , "content" : "北京明天天气怎么样?" } ,
message , # LLM 的工具调用请求
{
"role" : "tool" ,
"tool_call_id" : tool_call . id ,
"content" : json . dumps ( result ) # 函数执行结果
}
]
# 再次调用 LLM,让它根据结果生成回复
final_response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = messages
)
print ( final_response . choices [ 0 ] . message . content )
# "北京明天是晴天,温度 20 度。" 实际应用案例
案例 1:查询天气
完整代码示例:
import openai
import json
import requests
# 定义工具
tools = [ {
"type" : "function" ,
"function" : {
"name" : "get_weather" ,
"description" : "获取指定城市的天气信息" ,
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"city" : { "type" : "string" , "description" : "城市名称" } ,
"date" : { "type" : "string" , "enum" : [ "today" , "tomorrow" ] }
} ,
"required" : [ "city" ]
}
}
} ]
# 实际函数
def get_weather ( city , date = "today" ) :
# 模拟 API 调用
return { "city" : city , "date" : date , "temp" : 20 , "condition" : "晴" }
# 用户输入
user_input = "北京明天天气怎么样?"
# 第一次调用 LLM
response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [ { "role" : "user" , "content" : user_input } ] ,
tools = tools
)
message = response . choices [ 0 ] . message
# 如果有工具调用
if message . tool_calls :
tool_call = message . tool_calls [ 0 ]
function_name = tool_call . function . name
function_args = json . loads ( tool_call . function . arguments )
# 执行函数
result = get_weather ( ** function_args )
# 第二次调用 LLM(带上工具结果)
final_response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [
{ "role" : "user" , "content" : user_input } ,
message ,
{ "role" : "tool" , "tool_call_id" : tool_call . id , "content" : json . dumps ( result ) }
]
)
print ( final_response . choices [ 0 ] . message . content )
# "北京明天是晴天,温度 20 度。" 案例 2:多工具调用(发送邮件 + 添加日历)
场景: "提醒我明天下午 3 点开会,并给张三发邮件通知"
工具定义:
tools = [
{
"type" : "function" ,
"function" : {
"name" : "send_email" ,
"description" : "发送邮件" ,
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"to" : { "type" : "string" } ,
"subject" : { "type" : "string" } ,
"body" : { "type" : "string" }
} ,
"required" : [ "to" , "subject" , "body" ]
}
}
} ,
{
"type" : "function" ,
"function" : {
"name" : "add_calendar_event" ,
"description" : "添加日历事件" ,
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"title" : { "type" : "string" } ,
"time" : { "type" : "string" } ,
"date" : { "type" : "string" }
} ,
"required" : [ "title" , "time" , "date" ]
}
}
}
] LLM 可能的响应:
{
"tool_calls" : [
{
"function" : {
"name" : "add_calendar_event" ,
"arguments" : "{\"title\": \"会议\", \"time\": \"15:00\", \"date\": \"明天\"}"
}
} ,
{
"function" : {
"name" : "send_email" ,
"arguments" : "{\"to\": \"zhangsan@example.com\", \"subject\": \"会议通知\", \"body\": \"明天下午3点开会\"}"
}
}
]
} 执行流程:
# LLM 一次性请求调用两个工具
for tool_call in message . tool_calls :
if tool_call . function . name == "send_email" :
args = json . loads ( tool_call . function . arguments )
send_email ( ** args )
elif tool_call . function . name == "add_calendar_event" :
args = json . loads ( tool_call . function . arguments )
add_calendar_event ( ** args ) 案例 3:代码执行(Code Interpreter)
场景: "帮我计算 1 到 1000 的质数个数"
工具定义:
{
"name" : "execute_python" ,
"description" : "执行 Python 代码并返回结果" ,
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"code" : { "type" : "string" , "description" : "要执行的 Python 代码" }
} ,
"required" : [ "code" ]
}
} LLM 调用:
{
"function" : "execute_python" ,
"arguments" : {
"code" : "count = 0\nfor num in range(2, 1001):\n is_prime = True\n for i in range(2, int(num**0.5) + 1):\n if num % i == 0:\n is_prime = False\n break\n if is_prime:\n count += 1\nprint(count)"
}
} 执行并返回:
def execute_python ( code ) :
# 安全执行 Python 代码(沙箱环境)
result = subprocess . run ( [ 'python' , '-c' , code ] , capture_output = True , text = True )
return result . stdout
result = execute_python ( code )
# 输出:"168" 最终回复:
"1 到 1000 之间有 168 个质数。"
高级特性
1. 并行工具调用(Parallel Function Calling)
GPT-4 Turbo 支持:
{
"tool_calls" : [
{ "function" : { "name" : "get_weather" , "arguments" : "{\"city\": \"北京\"}" } } ,
{ "function" : { "name" : "get_weather" , "arguments" : "{\"city\": \"上海\"}" } } ,
{ "function" : { "name" : "get_weather" , "arguments" : "{\"city\": \"广州\"}" } }
]
} 优点:
一次性调用多个工具
减少 LLM 调用次数
提高效率
2. 强制工具调用
response = openai . chat . completions . create (
model = "gpt-4" ,
messages = [ { "role" : "user" , "content" : "今天星期几?" } ] ,
tools = tools ,
tool_choice = {
"type" : "function" ,
"function" : { "name" : "get_current_date" }
}
) 用途:
确保 LLM 一定调用某个工具
适用于必须查询数据的场景
3. 工具链(Tool Chaining)
场景: 复杂任务需要多步骤
示例: "帮我订一张明天去上海的机票"
流程:
1. LLM 调用:search_flights(from="北京", to="上海", date="明天")
→ 返回航班列表
2. LLM 生成:"找到 3 个航班,推荐 CA1234(800 元),需要预订吗?"
3. 用户:"好的"
4. LLM 调用:book_flight(flight_no="CA1234")
→ 返回预订成功
5. LLM 生成:"已预订 CA1234,请查收邮件。"
主流模型支持情况
模型 支持 Function Calling 并行调用 备注 OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo ✅ ✅ 最强支持 OpenAI GPT-4 ✅ ❌ 仅单次调用 OpenAI GPT-3.5-turbo ✅ ❌ 支持但不稳定 Anthropic Claude 3.5 ✅ ✅ Tool Use(官方名称) Google Gemini 1.5 Pro ✅ ✅ Function Calling Mistral Large ✅ ✅ 支持 LLaMA 3 ❌ ❌ 需微调
Function Calling vs Plugins vs Agents
特性 Function Calling Plugins Agents 定义 LLM 调用预定义函数 第三方服务集成 自主决策和执行 控制权 开发者 插件提供商 LLM 复杂度 低 中 高 灵活性 低(仅限预定义) 中 高 典型应用 查天气、发邮件 ChatGPT Plugins AutoGPT
关系:
Function Calling(基础能力)
↓
Plugins(封装好的工具包)
↓
Agents(自主调用工具链完成复杂任务)
最佳实践
1. 工具描述要清晰
❌ 差描述:
{
"name" : "get_data" ,
"description" : "获取数据"
} ✅ 好描述:
{
"name" : "get_weather" ,
"description" : "获取指定城市的实时天气信息,包括温度、天气状况、湿度等。适用于用户询问天气相关问题时。"
} 2. 参数定义要详细
{
"parameters" : {
"type" : "object" ,
"properties" : {
"city" : {
"type" : "string" ,
"description" : "城市名称,必须是中文全称,如:北京、上海、深圳"
} ,
"date" : {
"type" : "string" ,
"description" : "日期,格式为:today(今天)、tomorrow(明天)或 YYYY-MM-DD" ,
"enum" : [ "today" , "tomorrow" ]
}
} ,
"required" : [ "city" ]
}
} 3. 处理错误情况
try :
result = get_weather ( ** function_args )
except Exception as e :
# 返回错误信息给 LLM
result = { "error" : str ( e ) , "message" : "无法获取天气信息" } 4. 安全考虑
危险工具需要确认:
if function_name == "delete_database" :
# 敏感操作,需要用户确认
user_confirmation = input ( "确认删除数据库?(yes/no): " )
if user_confirmation != "yes" :
result = { "error" : "操作已取消" }
else :
result = delete_database ( ** function_args ) 输入验证:
def send_email ( to , subject , body ) :
# 验证邮箱格式
if not re . match ( r"[^@]+@[^@]+\.[^@]+" , to ) :
return { "error" : "无效的邮箱地址" }
# 实际发送
. . . 常见问题
Q: Function Calling 会增加多少成本?
A:
每次工具调用 = 2 次 LLM 调用(判断 + 生成回复)
成本约为普通对话的 2-3 倍
但换来的是真实数据和实际执行能力
Q: LLM 会乱调用工具吗?
A:
可能性很小,但需要防范
建议:敏感操作加确认机制
使用 tool_choice="none" 禁止调用
Q: 如何让 LLM 更准确地选择工具?
A:
工具描述写清楚(最重要)
减少工具数量(< 10 个为佳)
给 LLM 更多上下文
Q: Function Calling 和 RAG 有什么区别?
A:
RAG :检索外部知识库,增强回答Function Calling :执行实际操作可以结合使用!
参考资料